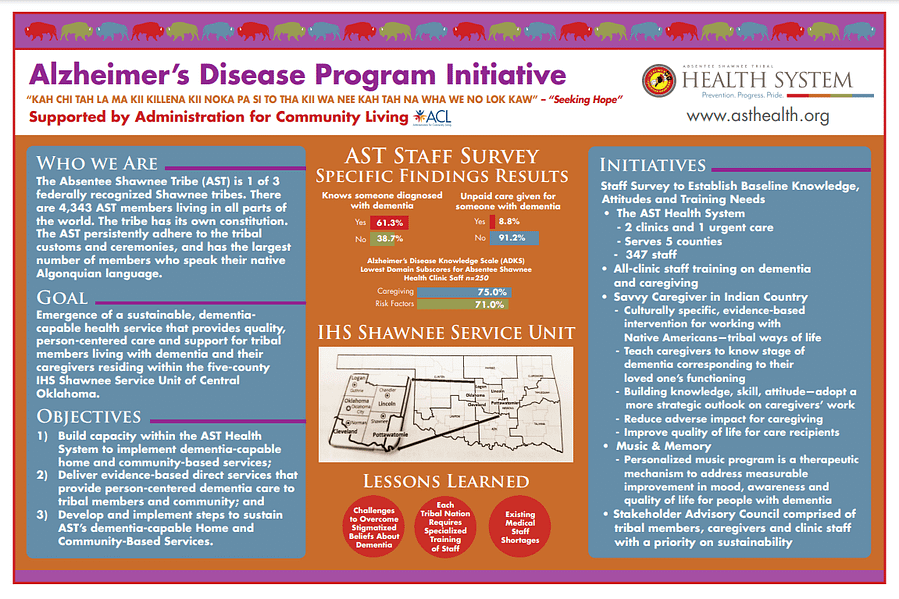
The Absentee Shawnee Tribe of Oklahoma and its Absentee Shawnee Tribal Health System are partnering to build a sustainable dementia-capable health service that provides quality, person-centered care and support for tribal members living with dementia and their caregivers within the five-county IHS Shawnee Service Unit of Central Oklahoma. The program is expected to improve the quality of life for people living with dementia and provide support for caregivers.
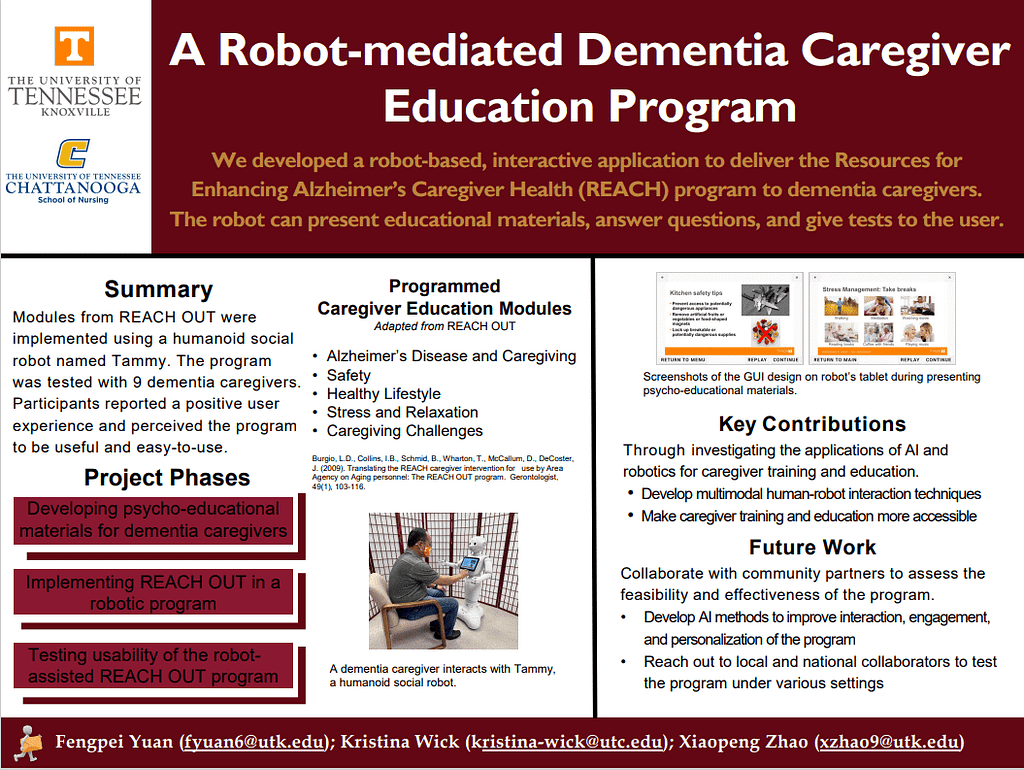
Long-duration, time-intensive dementia caregiving usually leads to increased risks of poor mental and physical health in caregivers. Using a humanoid social robot named Tammy, we developed an interactive robotic application to deliver the Resources for Enhancing Alzheimer’s Caregiver Health (REACH) program to dementia caregivers. The program is aimed to help caregivers prepare themselves for their roles during the caregiving journey by providing training and education. The robot can present educational materials, answer questions, and give tests to a user using multimodal interaction techniques. The program consists of five modules, including Alzheimer’s disease and caregiving, safety, healthy lifestyle, stress and relaxation, and caregiving challenges. We tested the program with nine dementia caregivers. Participants reported a positive user experience and perceived the program to be useful and easy-to-use. The results demonstrate the feasibility of the robot-mediated REACH program to enable the psychoeducational intervention more accessible to dementia caregivers and thereby support caregivers. Our next step is to develop advanced AI technology to improve interaction, engagement, and personalization of the robot-mediated program. Local and national collaborators will be sought out to test the feasibility and effectiveness program under various settings.
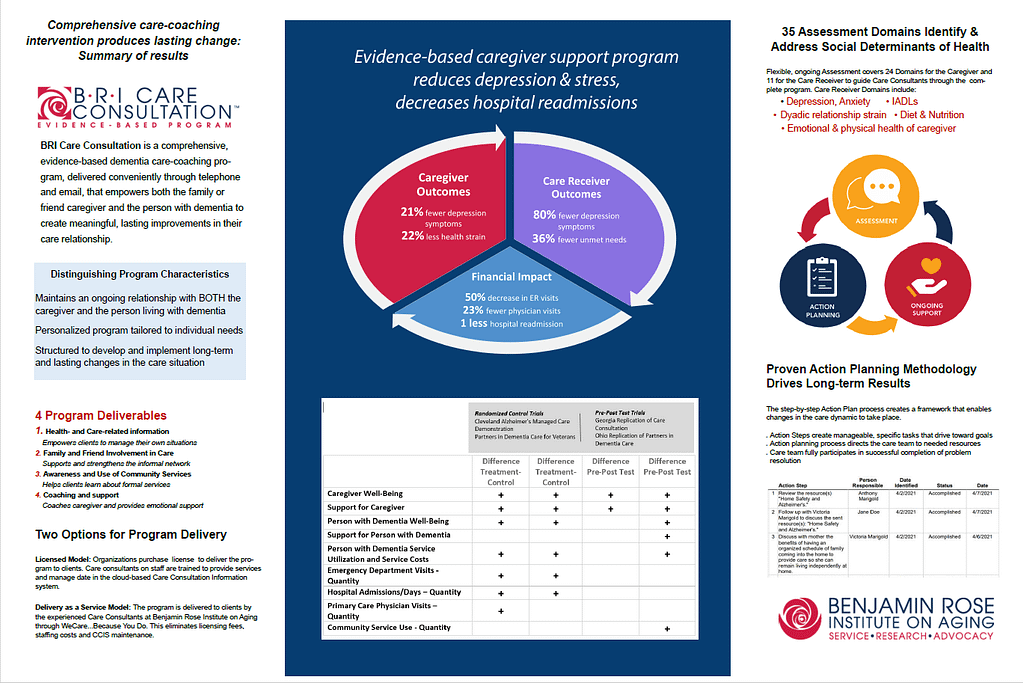
Established in 1961, the Center for Research and Education, part of the Benjamin Rose Institute on Aging, conducts state-of-the-art research to develop and deliver innovative, high-quality solutions to advance support for older adults and caregivers. Such research has resulted in the development of BRI Care Consultation, a comprehensive evidence-based dementia care-coaching program that addresses the needs of both the caregiver and the person receiving care. BRI Care Consultation has been the subject of multiple research studies over the past two decades, and has been shown in to produce outcomes of decreased feelings of depression in the care receiver, along with fewer hospital readmissions and ER visits. In the caregiver, results included decreased feelings of isolation and reduced strain on the caregiving relationship. More complete research findings can be accessed here: https://bpc.caregiver.org/#programDetails/bri-care-consultation. Research to further expand the reach of this program has been ongoing, including current grant funding from ACL to investigate the impact of the program on rural as opposed to urban environments, as well as its impact on the population of individuals with IDD with or at risk of dementia.
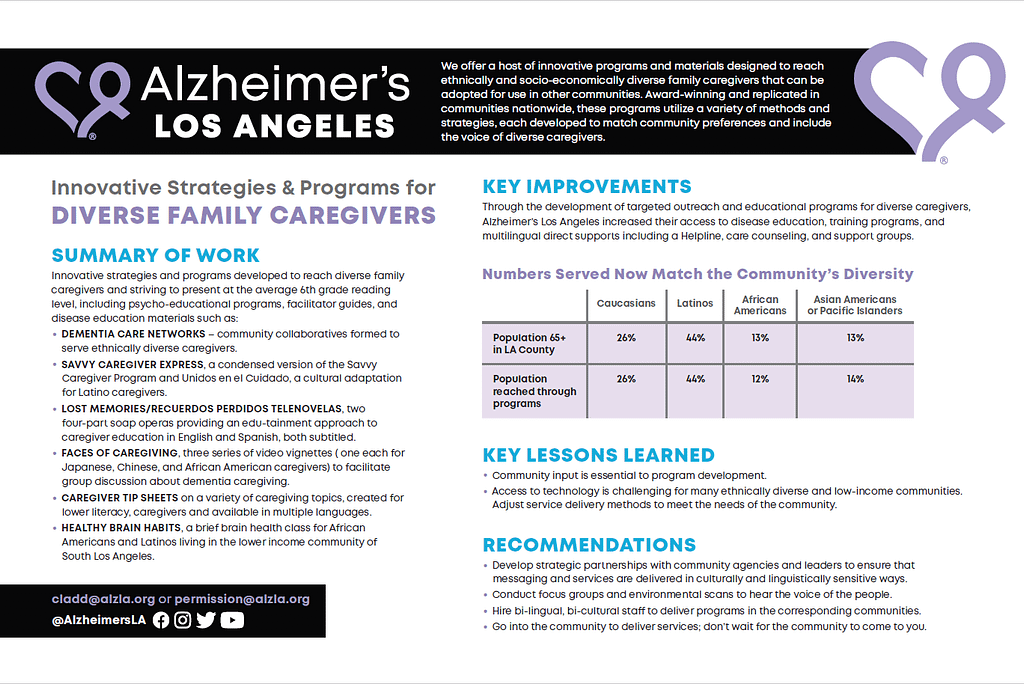
Alzheimer’s Los Angeles has developed innovative, easy to read materials and many programs to reach diverse family caregivers, including psycho-educational programs, multi-lingual caregiver videos, disease education and management materials. Award-winning and replicated in communities nationwide, these programs utilize a variety of methods and strategies, each developed to match community preferences and include the voices of diverse caregivers. Through the development of targeted outreach and use of these strategies, access to multilingual direct service supports was increased. Strategies included:
- Dementia Care Networks, Community collaboratives formed to serve ethnically diverse caregivers.
- Savvy Caregiver Express, a condensed version of the Savvy Caregiver Program and Unidos en el Cuidado, a cultural adaptation for Latino caregivers.
- Lost Memories/Recuerdos Perdidos Telenovelas, a two four-part subtitled soap opera with an edutainment approach to caregiver education in English and Spanish.
- Faces of Caregiving, three series of video vignettes (one each for Japanese-, Chinese- and African American caregivers) for group discussion about dementia caregiving.
- Caregiver Tip Sheets designed using quick, easy to read caregiving topics, and available in multiple languages.
- Healthy Brain Habits, a brief brain health class for African Americans and Latinos living in the lower income community of South Los Angeles.
USAging is the national association representing and supporting the network of Area Agencies on Aging and advocating for the Title VI Native American Aging Programs. As our members help older adults and people with disabilities throughout the United States live with optimal health, well-being, independence and dignity in their homes and communities, USAging administers multiple programs that are supportive of dementia caregiving efforts. Program highlights demonstrate the value and impact of social engagement resources, health care contracting tools and information and referral services. An overview of Dementia Friendly America (DFA) offers insight into how DFA communities influence change to foster support and enhance quality of life for people living with dementia and their care partners across the nation.
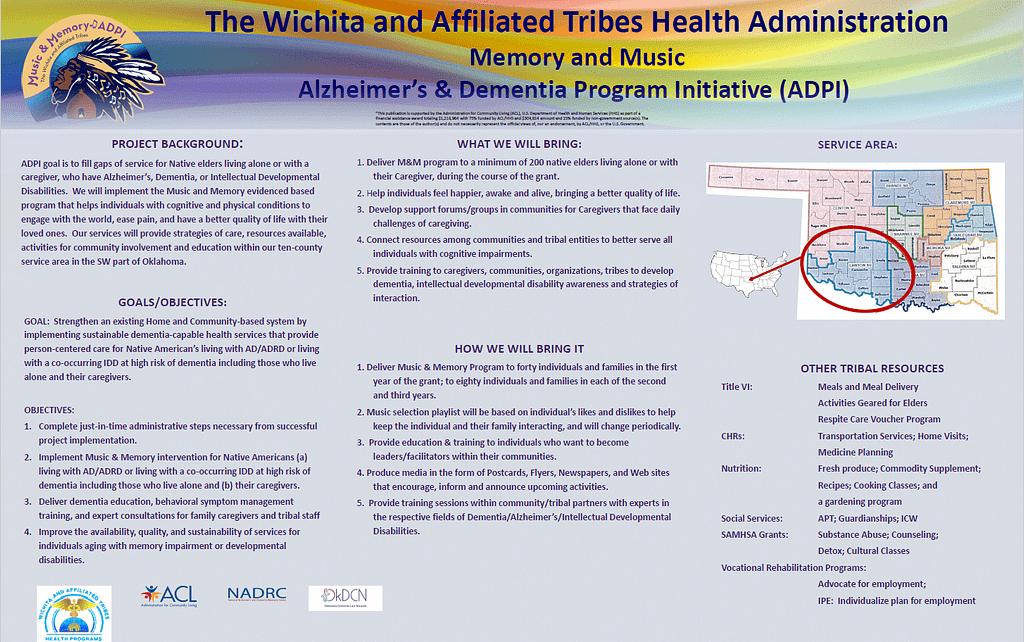
Music and Memory is an evidence-based program that helps individuals with cognitive and physical conditions to engage with the world, ease pain, and have a better quality of life with their loved ones. The Wichita and Affiliated Tribes Health Administration will implement the Music & Memory intervention to strengthen an existing Home and Community-Based System by implementing sustainable, dementia-capable health services that provide person-centered care for Native American’s living with AD/ADRD or living with a co-occurring IDD at high risk of dementia including those who live alone and their caregivers.
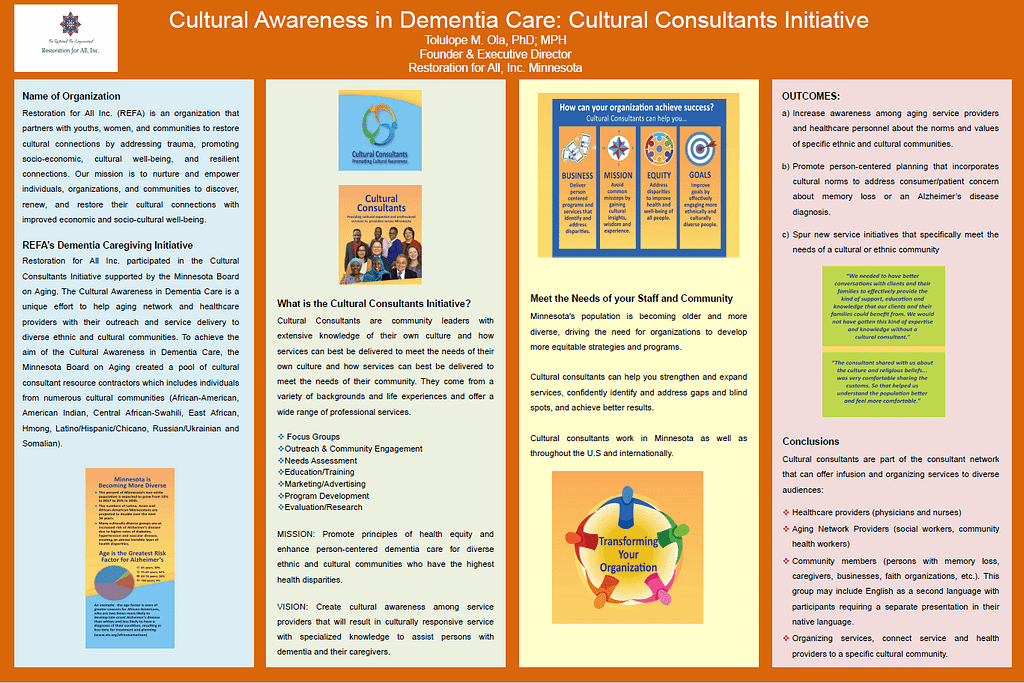
Restoration For All (REFA) is an organization that partners with youths, women, and communities to restore cultural connections by addressing trauma, promoting socio-economic, cultural well-being, and resilient connections. Its mission is to nurture and empower individuals, organizations, and communities to discover, renew, and restore their cultural connections with improved economic and socio-cultural well-being.
REFA participated in the Cultural Consultants Initiative supported by the Minnesota Board on Aging. Minnesota’s population is becoming older and more diverse, driving the need for organizations to develop more equitable strategies and programs. The Cultural Awareness in Dementia Care is a unique effort to help aging network and healthcare providers with their outreach and service delivery to diverse ethnic and cultural communities. To achieve the aim of the Cultural Awareness in Dementia Care, the Minnesota Board on Aging created a pool of cultural consultant resource contractors which includes individuals from numerous cultural communities (African American, American Indian, Central African-Swahili, East African, and Somali).
Development of a tailored digital platform to assist caregivers of persons living with dementia: Usability study
Logan DuBose1, Tokunbo Falohun1, Qiping Fan1, Minh-Nguyet Hoang1, David Doyle2, Novelle Kew1, Shinduk Lee3, Marcia Ory1
1 Texas A&M University
2 Central Michigan University
3 University of Utah
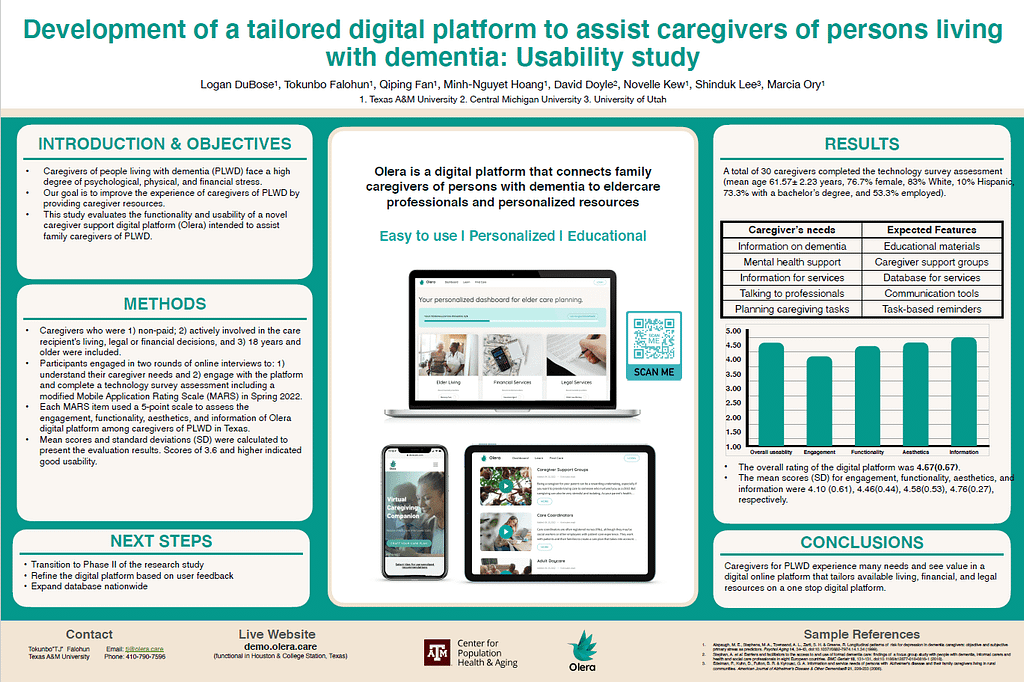
Objective: purpose of the study was to evaluate the functionality and usability of a novel caregiver support digital platform
(Olera) intended to assist family caregivers of people living with dementia (PLWD). Caregivers who were: 1) non-paid, 2) actively involved in the care recipient’s living, legal or financial decisions, and 3) 18 years and older) were included.
Participants in the usability study were engaged in two interview rounds to: 1) understand their caregiver needs and 2) engage with the platform and complete a technology survey assessment [modified Mobile Application Rating Scale (MARS)] via a Qualtrics online form. Each MARS item used a 5-point scale to assess the engagement, functionality, aesthetics, and information of Olera digital platform among unpaid caregivers of PLWD in Texas. Mean scores and standard deviations (SD) were calculated to present the evaluation results. Scores of 3.6 and higher indicated good usability.
Results: 29 caregivers completed the technology survey assessment (mean age 61.57± 2.23 years).
Overall rating of the digital platform was 4.57(0.57), and the mean scores (SD) for engagement, functionality, aesthetics, and information were 4.10(0.61), 4.46(0.44), 4.58(0.53), 4.76(0.27), respectively.
Conclusion: Olera is practical, interactive, easy to use, visually appealing, and informative digital platform to provide resources for caregivers of PLWD.
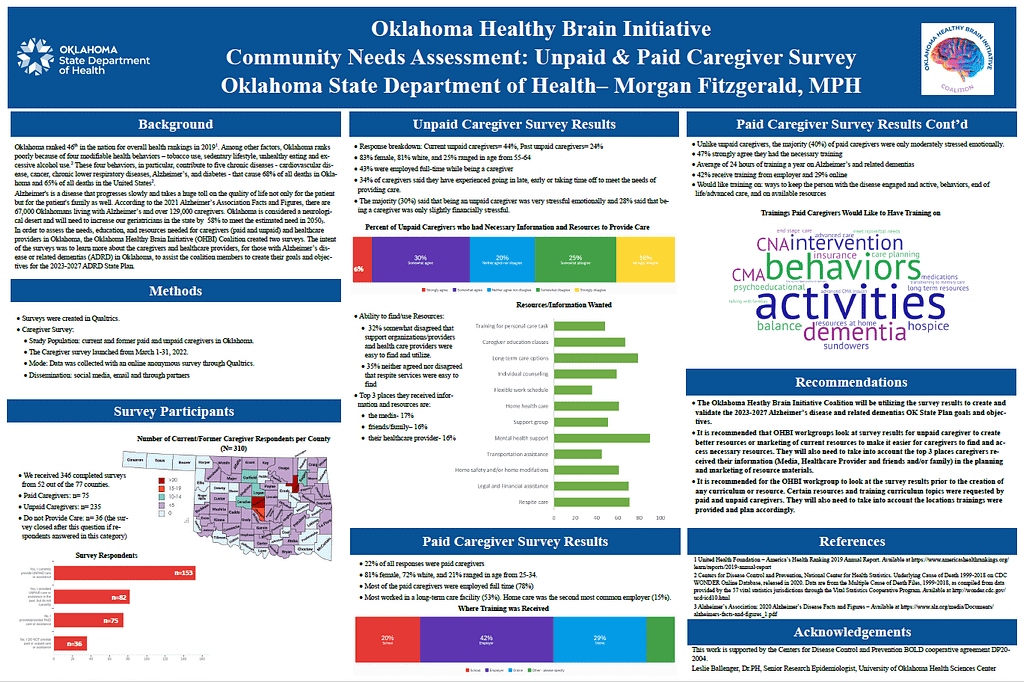
There are over 129,000 caregivers for those facing Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) in Oklahoma. The Oklahoma Healthy Brain Initiative (OHBI) Coalition wanted to better understand their needs in regard to resources and training to assist the coalition members to create their goals and objectives for the 2023-2027 ADRD State Plan.
Data was collected with an online survey through Qualtrics. The survey was disseminated via email, social media, and through partners. 346 completed Caregiver Surveys were received and 60 completed Provider Surveys. Preliminary data shows that only 30% of our unpaid caregiver felt they had the necessary information and resources and the top resource they would like more information is on mental health support. Unpaid caregivers informed that the majority receive their training via their employer and gave topics for future trainings. The OHBI will take into consideration the topics for resources and trainings provided by the paid
and unpaid caregivers when creating goals/objectives for the updated 2023-2027 ADRD State Plan and printed materials.
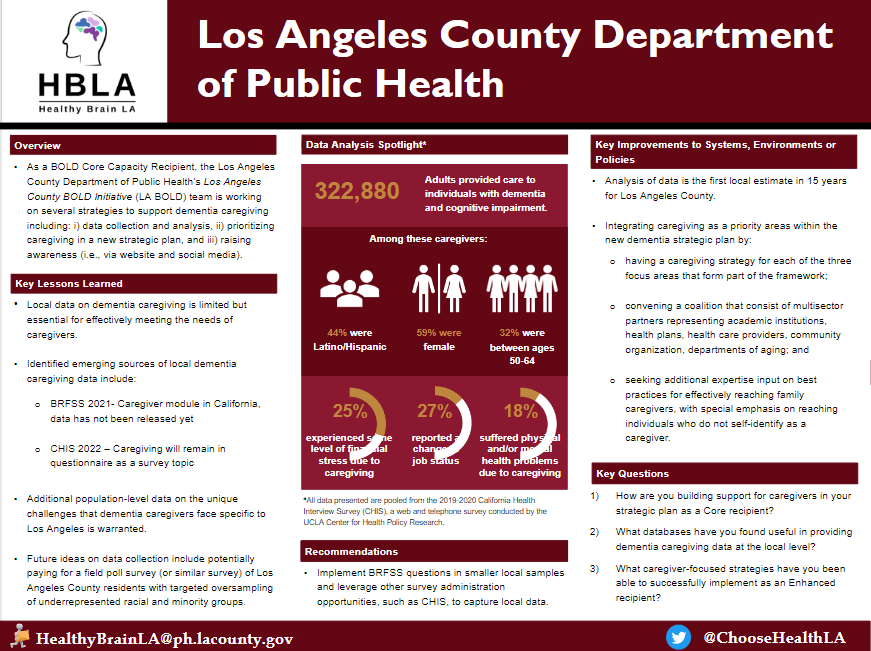
The Los Angeles County Department of Public Health’s Los Angeles County BOLD Initiative (LA BOLD) team is working on several strategies to support dementia caregiving including: i) data collection and analysis, ii) prioritizing caregiving in a new strategic plan, and iii) raising awareness. This poster showcases an analysis of 2019-2020 California Health Interview Survey data on adult caregivers of individuals with dementia/cognitive impairment.
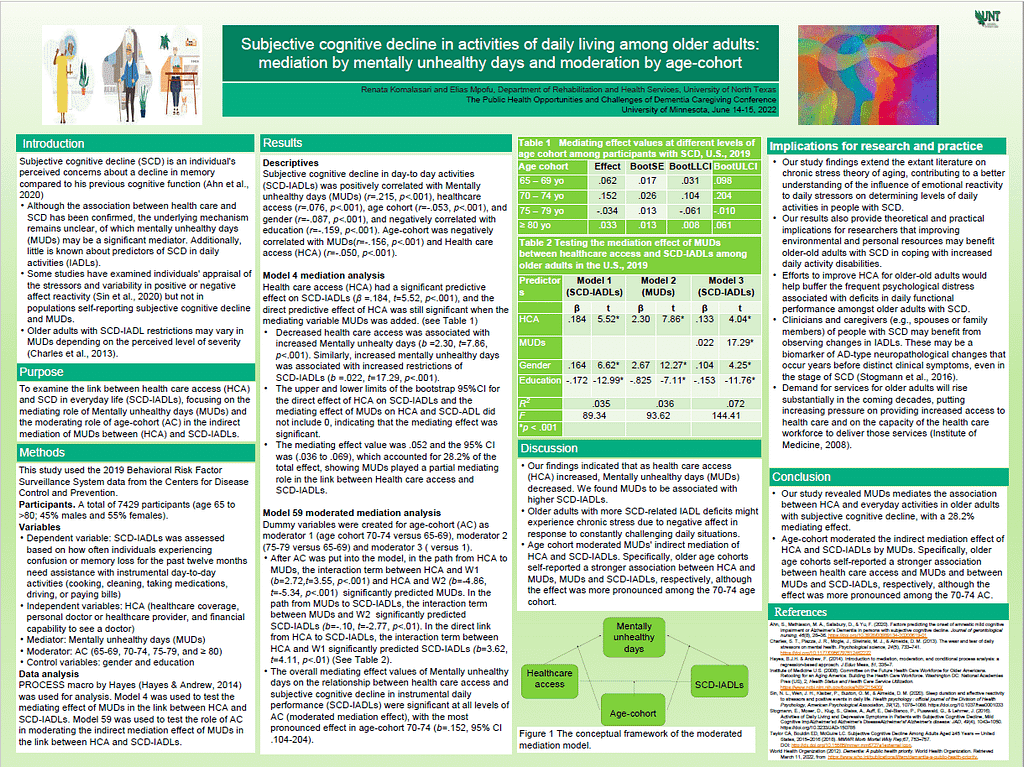
Subjective cognitive decline in older adults is associated with decreases in quality of daily living, although this may vary by age cohort and comorbid conditions. The purpose of this study is to explore the mediating effect of mental wellbeing (MW) and the role of age-cohort as a moderator in the relationship between healthcare access (HCA) and activities of daily living (ADL) among older adults with subjective cognitive decline (SCD-ADL).
This study used the 2019 CDC BRFSS data, self-reported responses to questions assessing ADL, HCA, MW, and AC. Bootstrap analyses were employed to explore the mediating effect of MW and the moderating role of AC on HCA and SCD-ADL. 7429 participants were included in the study (age 65 to >80; 45% males, 55% females).
After controlling for gender and education, MW partially mediated the effect of HCA on SCD-ADL (indirect effect=.52, 95% CI .36 to .69), with the mediating effect accounting for 28.2% of the total effect. Age-cohort moderated the relationship between HCA and MW, HCA and SCD-ADL, and MW and SCD-ADL, with the strongest effect in age cohort 70-74 years old (β=.152, 95%CI .104-.204).
This study supports potential mechanisms in the association between HCA and SCD-ADL. The young to middle-old cohort appears to moderate the indirect effect of MW on the association between HCA and SCD-ADL. This study supports potential mechanisms in the association between HCA and SCD-ADL. Improving access to healthcare for the aging population might improve ADL for older adults with SCD.
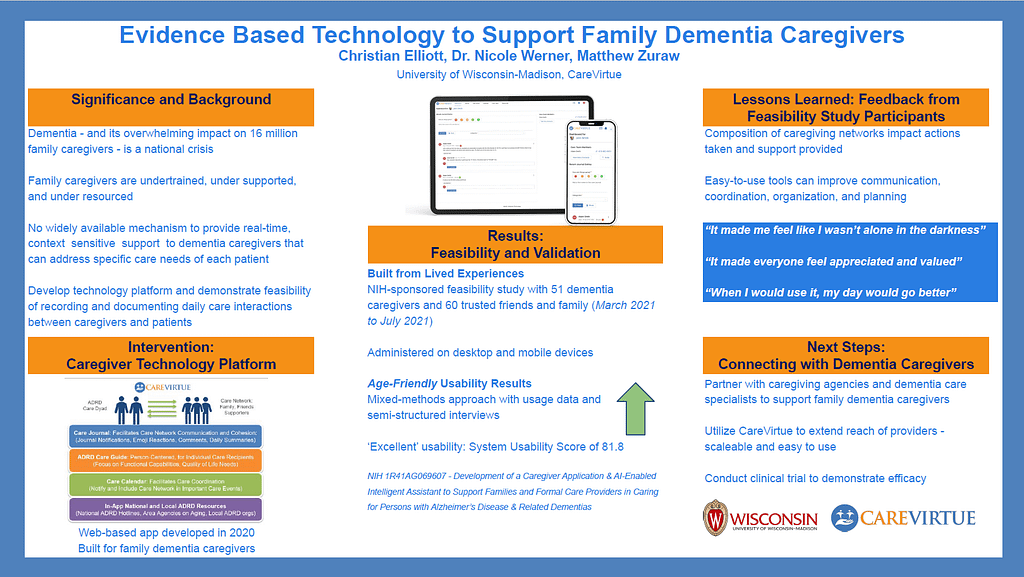
CareVirtue is a novel caregiving platform, private social network, and legal & financial planner built for dementia caregivers.
CareVirtue conducted a NIH-sponsored feasibility study with 51 dementia caregivers and we are building our legal & financial planner based on living experiences for caregivers. The feasibility results establish acceptability and usability of CareVirtue for caregivers. The age-friendly platform received a System Usability Scale score of 81.8, indicating ‘excellent’ usability and interviews showed CareVirtue was helpful, including practically, organizationally, and emotionally.
Caregivers used CareVirtue to coordinate and communicate. They felt CareVirtue supported collaboration, heightened their own awareness, and helped them feel seen and appreciated.
CareVirtue learned that personal caregiving networks impact the actions taken to support people living with dementia. Collaborating with caregiving-focused agencies created connections with dementia caregivers in communities across the country. Development of partnerships with community agencies and dementia care specialists will enhance the reach of CareVirtue.
Caregivers can be supported with easy-to-use tools that improve communication, coordination, organization, and planning. Community agencies can benefit from CareVirtue by making support easier to track and understand. To advance initiatives, we need to gain more understanding of how to help caregivers take steps now to ease the burden of providing care.
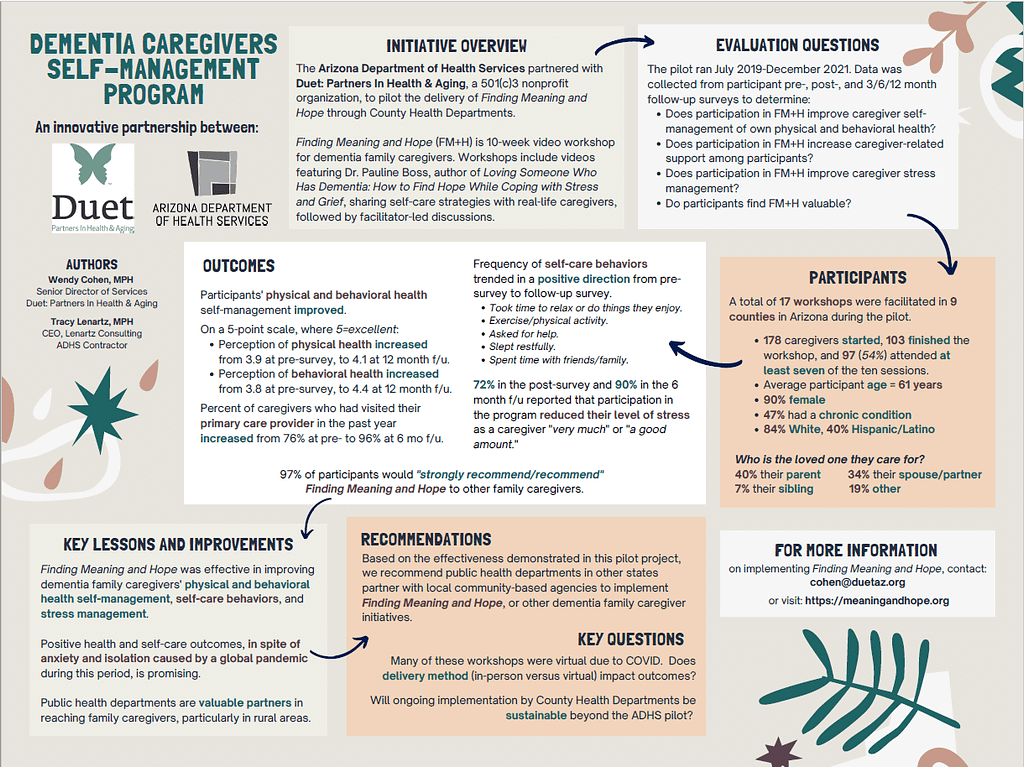
In 2019, the Arizona Department of Health Services piloted Duet: Partners In Health & Aging’s (a 501(c)3 nonprofit) Finding Meaning and Hope 10-week video workshop for dementia family caregivers, to promote understanding of grief and teach stress-mitigating self-care concepts. Workshops include videos featuring Dr. Pauline Boss, author of Loving Someone Who Has Dementia: How to Find Hope While Coping with Stress and Grief, sharing self-care strategies with real-life caregivers, followed by facilitator-led discussions. Through December 2021, 103 caregivers completed the programs (13 English, 4 Spanish) delivered by 9 county health departments, 90% were female, 84% were white, 40% were Hispanic/Latino, with an average age of 61.1 years and 47% self-reported a chronic illness. 148 pre- and 89 post-series surveys were completed. Five self-care measures trended in a positive direction from pre to follow-up survey. The majority (72% in the post-survey, 56% at 3 months after, 90% at 6 months and 69% at 12 months) reported that participation in the program reduced their level of stress as a caregiver "very much/a good amount." This positive movement, despite the anxiety and isolation many experienced during the pandemic, is promising and demonstrates the positive impact of an innovative public health collaboration.
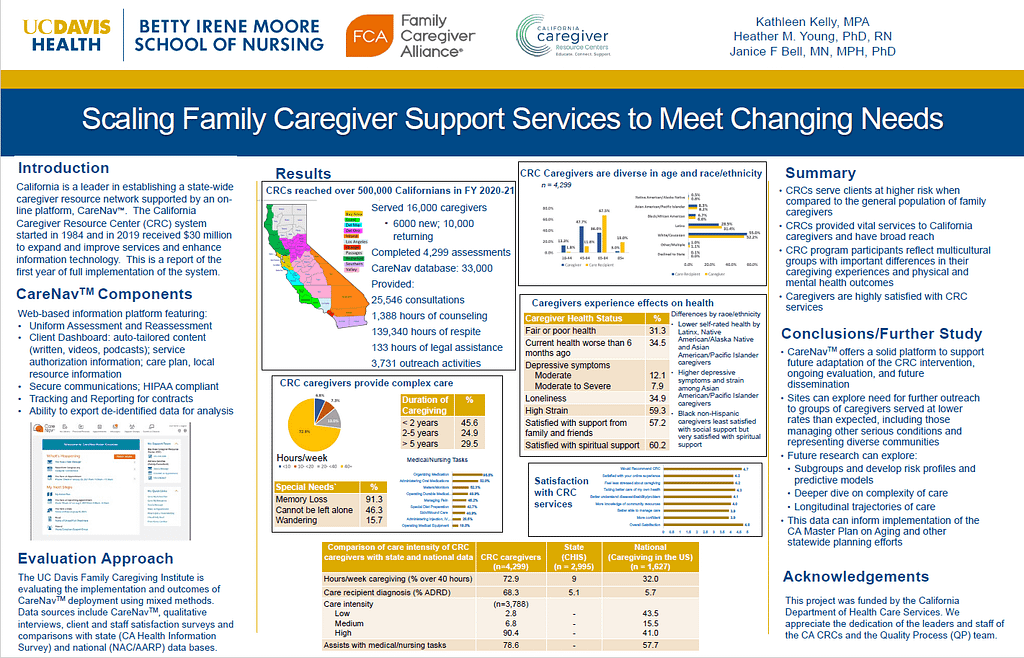
California is a leader in establishing a state-wide caregiver resource network supported by an on-line platform, CareNavTM. The California Caregiver Resource Center (CRC) system started in 1984 and in 2019 received $30 million to expand and improve services and enhance information technology. This is a report of the
first year of full implementation of the system.
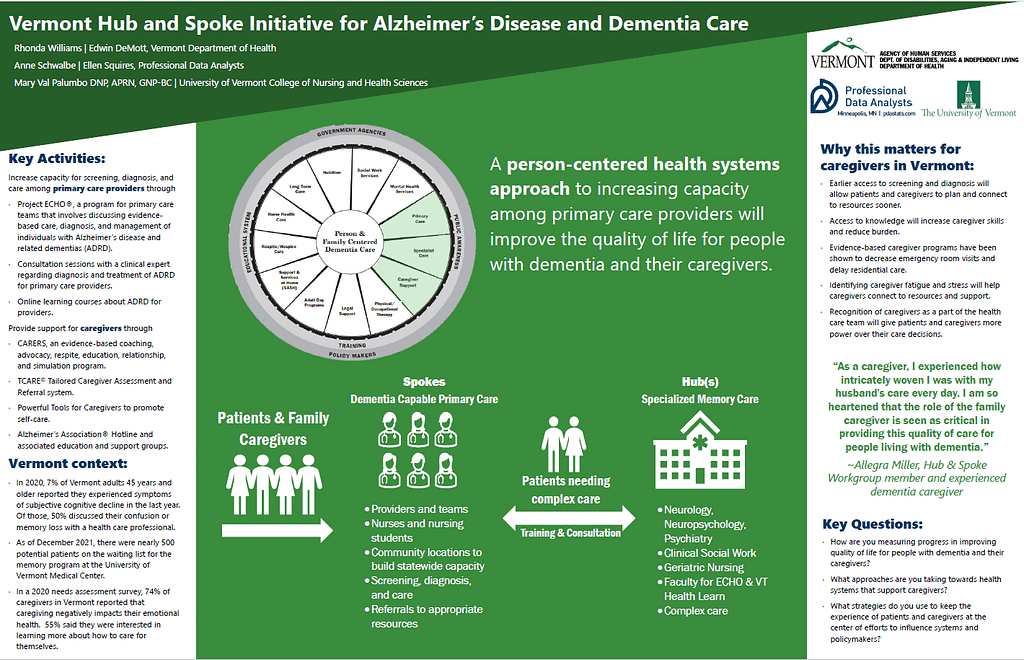
The Vermont Hub and Spoke Initiative is an effort to increase screening, diagnosis, and care for people in Vermont living with Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias (ADRD) and their caregivers by increasing capacity among primary care providers. The Hub and Spoke Initiative for ADRD is a health systems interprofessional approach providing evidence-based training and consultation for primary care providers and support and recognition for caregivers as members of the health care team. The Initiative aims to keep the experience of patients and caregivers at the center of the work while also including health system decision makers in planning next steps for dementia care in Vermont.
The State of Nevada, through the CDC BOLD grant, is partnering with the University of Nevada, Reno Dementia Engagement, Education, and Research (DEER) Program, the home base of the statewide Dementia Friendly Nevada (DFNV) initiative, to engage key stakeholders, including people living with dementia, in the collaborative development and advancement of innovations and improvements to support growing care systems, strengthen the education and support available to people living with dementia and their care partners, improve training for healthcare and public health professionals, and raise public awareness about brain health, risk reduction, and Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD). The State of Nevada has made progress in sustaining dementia caregiving efforts and has gained valuable lessons in the process of community collaboration with people living with dementia and their care partners, stakeholders, and healthcare professionals. Nevada continues to find engaging, inclusive, and dementia-friendly ways to develop community goals and leverage technology.
Central Minnesota Dementia Community Action Network (D-CAN) is a nonprofit organization that provides integrated dementia patient care (and caregiver/family support) at our Dementia Resource Center (DRC) and Memory Loss Clinic in St. Cloud, Minnesota. In addition to doing medical evaluations and working closely with the patient’s primary care and specialty clinicians, we provide an adaptable working care plan that is usable by all clinicians and support services providers. We also follow the patient’s continuing care via quarterly follow-up visits and provide ongoing support to the patient’s clinician(s), caregivers, family and loved ones. Thanks to the generosity of our philanthropic supporters and the commitment and generosity of our medical professional volunteer team members, we provide service to all and do not charge for our services, beyond what may be reimbursable by Medicare, Medicaid, private insurance, and we even welcome those with no insurance.
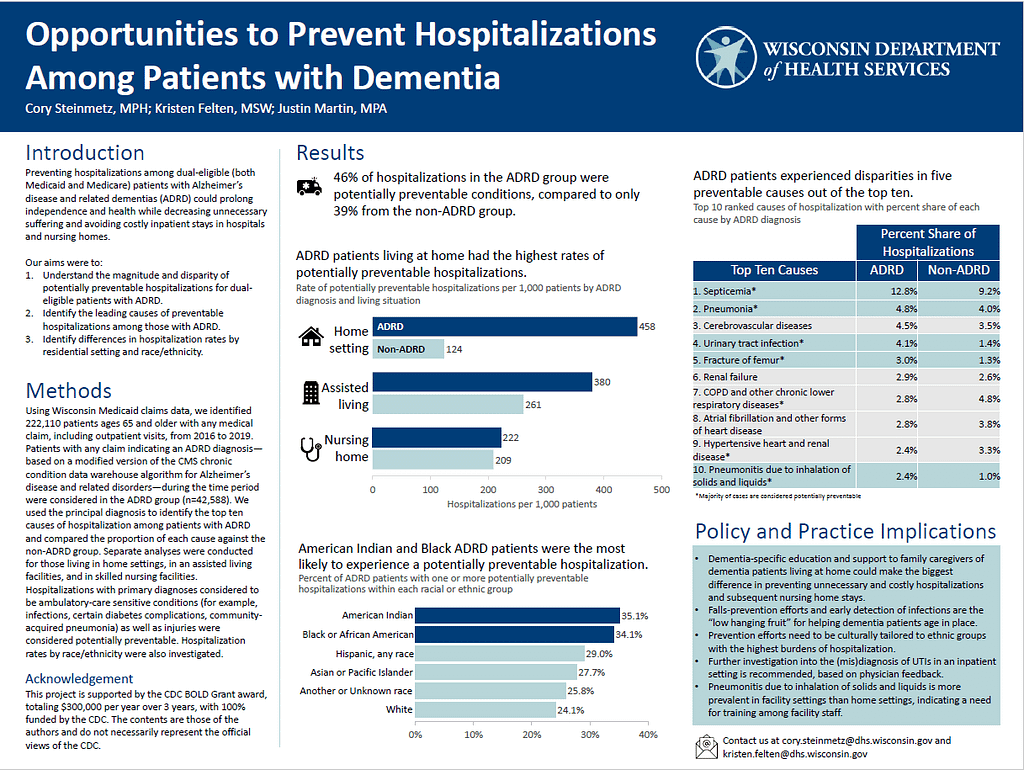
Family caregivers of people with dementia often do not have the training or support to be able to recognize when the person they are caring for has a developing health condition they should address, or how to prevent the most common co-occurring conditions that accompany dementia. The Wisconsin Department of Health Services performed a retrospective claims analysis from 2016 through 2019 of individuals with a dementia diagnosis to determine the prevalence of preventable hospitalizations and the most common causes by living situation. Individuals were found to be admitted to the hospital for undetected infections and inhalation pneumonia when residing at home more often than other conditions. One solution could be providing family caregivers of people with dementia information, training and support to know how to recognize and prevent these conditions from occurring or leading to a hospitalization. Reduced incidence of preventable illness and hospitalizations improve quality of life for both the person with dementia and the family caregiver, and the knowledge and information given to caregivers can help them to feel more capable in their role
The Minnesota Department of Health Healthy Brain Initiative has focused on building partnerships and collaboration related to dementia risk reduction, early detection, and caregiver support. In 2022, we established the Minnesota Healthy Brain Partnership to coordinate efforts among dementia focused organizations in Minnesota, promote culturally responsive strategies, and leverage statewide resources. We have also engaged local public health, community-based organizations, and primary care organizations to plan and implement strategies to enhance the caregiver support infrastructure in Minnesota.
This poster highlights the goals and plan for the “Together Strong” project of the Great Lakes Intertribal Council, Wisconsin. Together Strong seeks to develop a comprehensive network of education, referrals and person-centered services for tribal members suspected or living with AD/ADRD and their family caregivers; implement best practices for dementia-friendly tribal communities and address health disparities in home and community-based services for people living with dementia and their caregivers.
IA2 is funded as a national hub for dementia and Alzheimer’s information resources serving Indian country, Alaskan Villages, and urban Indian populations using public health approaches. Activities are designed to advance community engagement and help build capacity among tribes and tribal member-serving organizations, promote healthy cognitive aging strategies across the lifespan, and foster dementia-capable tribal communities. The Healthy Brain Initiative’s Road Map for Indian Country serves as a guide for project activities. This poster provides an overview of available services, products that have been created and that are under development, and a summary of year one accomplishments. This project is funded by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
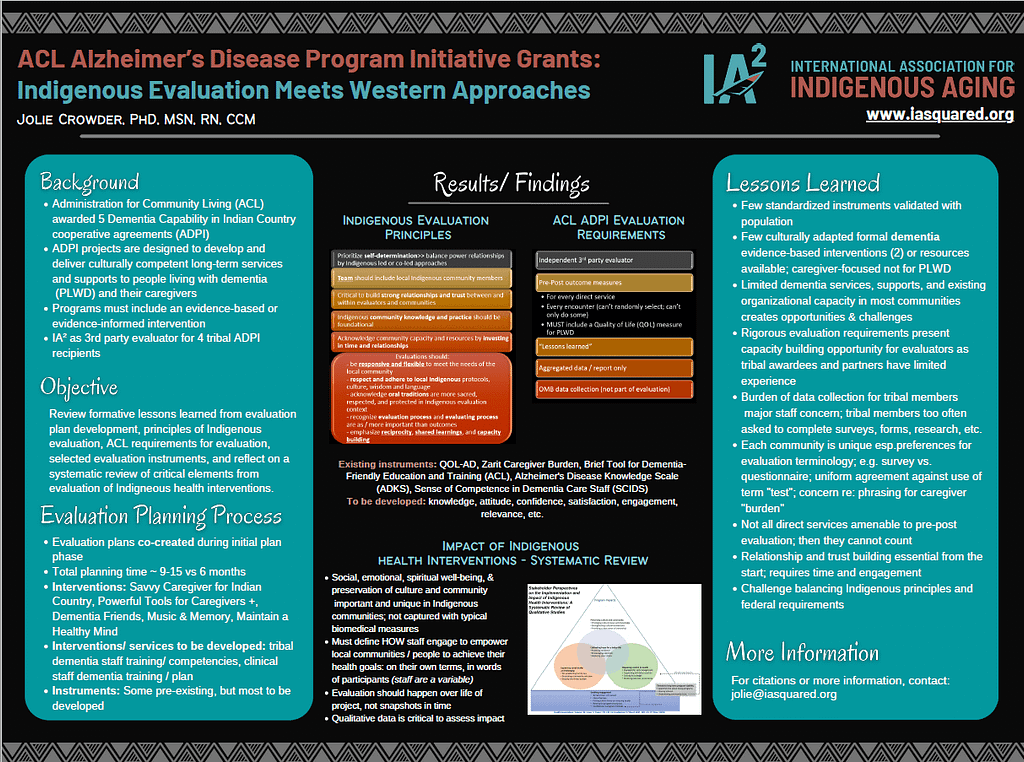
This poster provides an overview of common experiences and early lessons from serving as a third-party evaluator for multiple Administration for Community Living (ACL) Alzheimer’s Disease Program Initiative (ADPI) Dementia Capability in Indian Country awardees. The International Association for Indigenous Aging currently partners with four of five Indian country ADPI awardees. ADPI programs are designed to develop and deliver culturally competent long-term services and supports to people living with dementia and their caregivers. Programs must include an evidence-based or evidence-informed intervention. Poster content will reflect a review of principles of indigenous evaluation, ACL requirements and resources for project evaluation, instruments planned for use that have been tested with indigenous communities, and reflection on a recent research review of critical elements of indigenous evaluation.
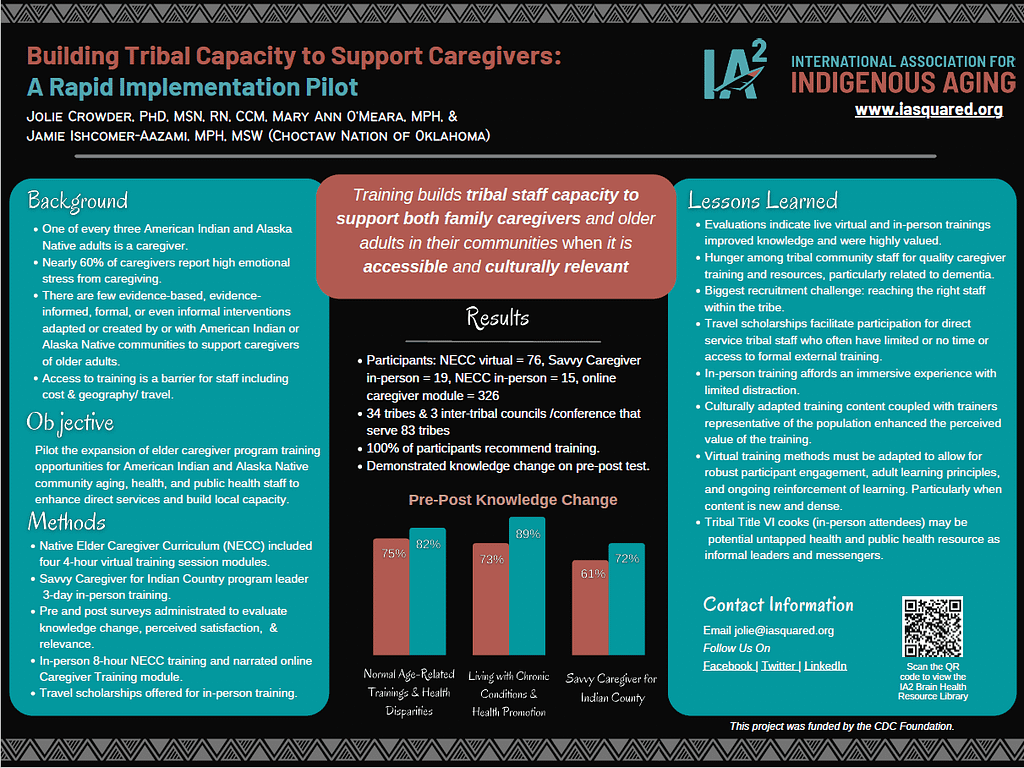
This poster provides an overview of a short-term pilot project funded by the CDC Foundation designed to build tribal capacity by extending two existing culturally relevant caregiving training programs to tribal staff and community members. One of every three American Indian and Alaska Native adults is a caregiver. About half of caregivers provide unpaid care for almost 20 hour per week and do so for someone with dementia or Alzheimer’s. Nearly 60% of dementia caregivers report high emotional stress from caregiving. Caregivers with high burden also report they neglect self-care, have higher risk of serious illnesses (like cancer, diabetes, etc.), increased death for their spouses, are less likely to get preventive care, have more anxiety, financial problems, etc. There are few evidence-based, evidence-informed, formal or even informal interventions adapted or created by, for, or with American Indian or Alaska Native communities to support caregivers of older adults. This pilot program was designed to eliminate geographic and financial barriers for tribal and Alaska Native aging, health, and public health staff to enable participation in caregiver training and train-the-trainer activities.
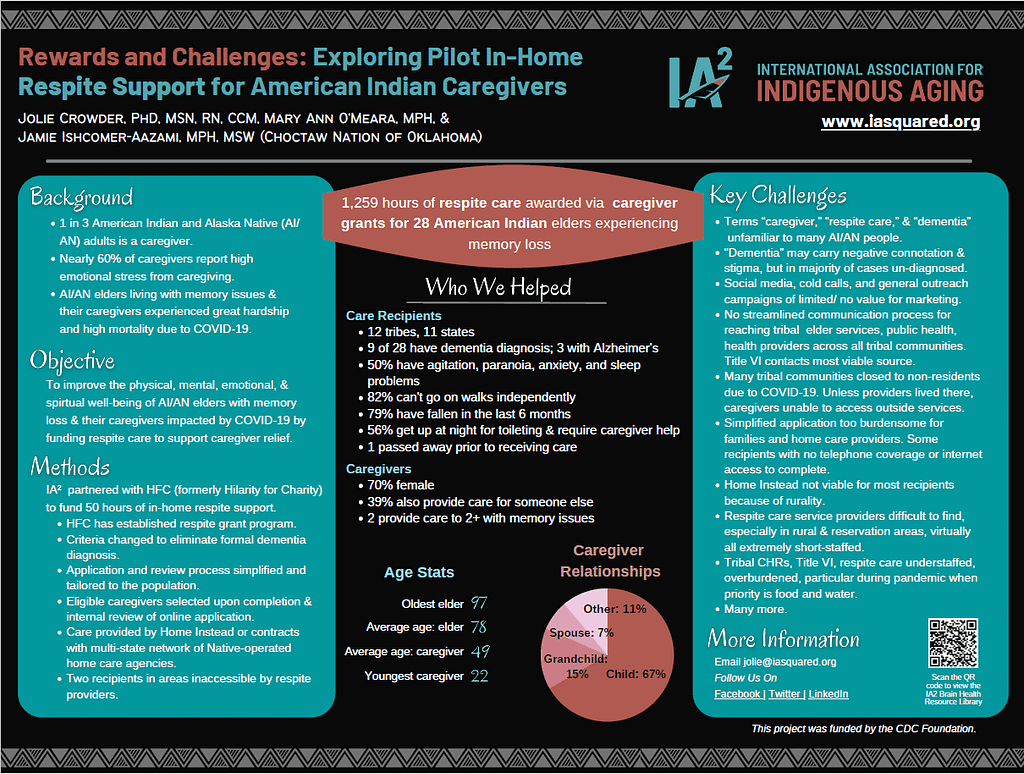
Reservation and community lockdowns, staffing shortages, and unknown terminology all proved to be barriers to a pilot project focused on getting in-home support for caregivers of Native elders experiencing memory loss. One of every three American Indian and Alaska Native adults is a caregiver. About half of caregivers provide unpaid care for almost 20 hour per week and do so for someone with dementia or Alzheimer’s. Nearly 60% of dementia caregivers report high emotional stress from caregiving. Caregivers with high burden also report they neglect self-care, have higher risk of serious illnesses (like cancer, diabetes, etc.), increased death for their spouses, are less likely to get preventive care, have more anxiety, financial problems, etc. A short-term pilot project funded by the CDC Foundation helped 28 American Indian caregivers and their families by funding 1,259 hours of respite care. This poster examines challenges, rewards, and lessons learned to implement the respite care grant program amid a global pandemic.